The 2023 NTI Nuclear Security Index
“The bottom line is that the countries and areas with the greatest responsibility for protecting the world from a catastrophic act of nuclear terrorism are derelict in their duty,” the 2023 NTI Index reports.
“The bottom line is that the countries and areas with the greatest responsibility for protecting the world from a catastrophic act of nuclear terrorism are derelict in their duty,” the 2023 NTI Index reports.
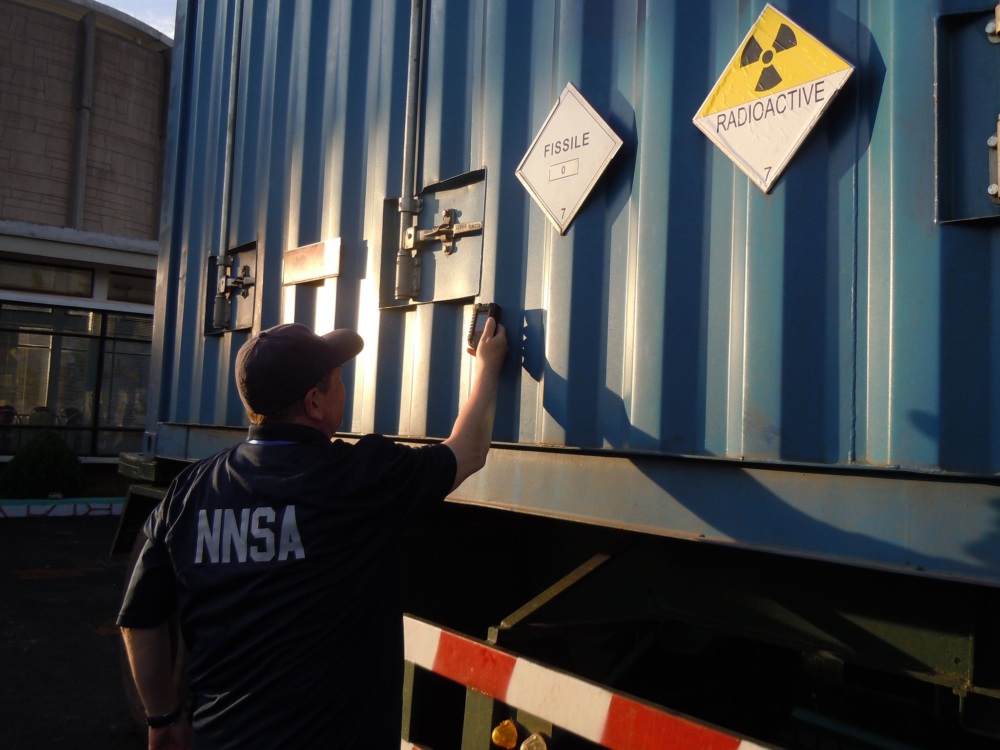
Nuclear and radiological security aims to ensure nuclear and other radioactive materials are secure from unauthorized access and theft, and that nuclear facilities are secure from sabotage.
Decision makers in the United States and across the world are taking steps to eliminate the risk of dirty bombs through cesium-137 irradiator replacement.
Since the third edition of the 2016 NTI Nuclear Security Index, many countries have taken positive steps to improve their nuclear security conditions. NTI is tracking these improvements, which will be reflected in the next edition of the NTI Index.
NTI Executive Vice President Deborah Rosenblum discussed radiological risks at a meeting in Paris of the International Forum of Terrorism Risk (Re)insurance Pools.
This paper on strengthening the security of radiological sources has been prepared for the November 2016 Global Dialogue in Warrenton, VA.
Recent terrorist attacks have renewed concerns that terrorists could use widely available radiological sources to carry out an attack. Reducing the use of high-risk sources can help reduce this potential threat from occurring.
A tool kit to support undergraduate or graduate courses in international relations, security studies, diplomacy, counterterrorism, or nuclear sciences.
Chechen resistance movement's evolution during the 1990s and its potential for carrying out an act of radiological terrorism. (CNS)