North Korea

Country Spotlight
The world’s newest nuclear weapon possessing state, North Korea withdrew from the NPT in 2003 and conducted its first nuclear test in 2006. It has developed sophisticated nuclear weapons and ballistic missiles despite international condemnation, and diplomatic efforts to denuclearize the country have thus far been unsuccessful.
See North Korea's performance in
Region East Asia and the Pacific
~35-65 Current nuclear warhead stockpile estimates
6 Nuclear tests conducted, most recently in 2017
15,000 Kilometers estimated maximum range of Hwasong-18 ICBM
~56-70 Kilograms estimated plutonium inventory
Nuclear
- Tested likely thermonuclear device in 2017
- Agreed to a moratorium on nuclear and long-range missile testing in 2018; resumed long-range missile tests in 2020
- Produces enriched uranium and weapons-grade plutonium

Nuclear Disarmament North Korea
Biological
- Assessments of capabilities and intent are speculative and vary widely
- Accused by U.S. and South Korea of pursuing biological weapons despite treaty commitments
- Presumed capability to produce anthrax, smallpox and plague
North Korea Biological Overview
North Korea Biological Facilities
Missile
- Variety of land-based ballistic and cruise missiles; recent tests of ICBMs and short- and medium-range, solid-fueled missiles
- Tested first ICBM, the Hwasong-15, on 24 March 2017
- Exporter of ballistic missile technology to countries such as Egypt, Iran, Iraq, Pakistan, and Syria

North Korea Missile Facilities

The CNS North Korea Missile Test Database
Chemical
- Denies chemical weapons possession, but refuses to accede to Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC)
- South Korea estimates North Korea's stockpile at 2,500 – 5,000 tons of chemical weapons agents
- Weapons program has concentrated on acquiring mustard, phosgene, sarin, and VX

North Korea Chemical Facilities

Tutorial on Chemical Weapons Nonproliferation
Treaties and Regimes Memberships
- NTI
- CNS
 North Korea
North KoreaAtomic Energy Research Institute
- Nuclear
Chiha-ri Missile Base
- Missile
Geumchang-ri Underground Facility
- Nuclear
Geumho-Jigu Light Water Reactor Site
- Nuclear
Hagap Underground Suspected Nuclear Facility
- Nuclear
Hamheung University of Chemical Industry
- Chemical
January 18th Machine Factory
- Missile
Kim Il Sung University
- Nuclear
Kum Song Tractor Factory
- Missile
Kumcheon Scud Missile Base
- Missile
Kusŏng Machine Tool Factory
- Missile
MGC-20 Cyclotron
- Nuclear
No. 125 Factory
- Missile
No. 26 Factory
- Missile
No. Seven Factory
- Missile
Okp’yŏng-dong Missile Base
- Missile
P’yŏngsan Uranium Milling Facility
- Nuclear
Pakch’ŏn Uranium Mine
- Nuclear
Pukchung Machine Complex
- Missile
Punggye-ri Nuclear Test Facility
- Nuclear
Pyongyang Semiconductor Factory
- Missile
Sakkabbong Missile Base
- Missile
Sangnam-ri Missile Base
- Missile
Shin’o-ri Missile Base
- Missile
Sohae Satellite Launching Station
- Missile
Sŭngni Automobile Factory
- Missile
Taecheon 200MWe Nuclear Reactor
- Nuclear
Tonghae Satellite Launching Ground
- Missile
Yongbyon High-Explosive Test Site
- Nuclear
Yongbyon Nuclear Research Center
- Nuclear
Yongdeok-dong High-Explosive Test Site
- Nuclear
Yŏngjŏ-ri Missile Base
- Missile
Yongnim-ŭp Missile Base
- Missile
Analysis
North Korea

Does Kim Jong Un’s Phone Give a Window into North Korean Command-and-Control?
Kim Jong Un may use his smartphone for nuclear command-and-control, increasing the risk of accidental nuclear war between the US and North Korea. (CNS)
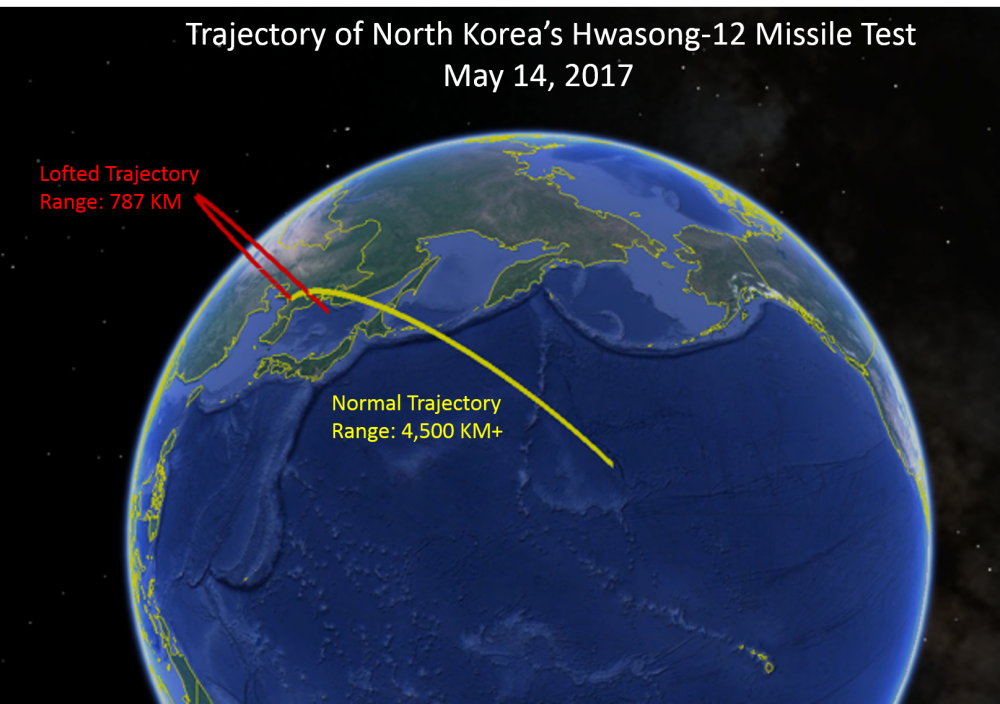
New Analysis and Interactives Uncover the Story of North Korea’s Missile Test

North Korea Submarine Capabilities

Education Center
