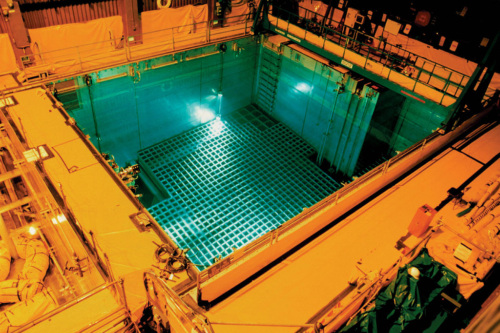
Developing Spent Fuel Strategies
Generating new solutions for spent fuel waste management and addressing broader fuel cycle concerns
Nuclear materials, whether used in weapons systems or for energy programs, are at risk of theft, sabotage, or diversion by state and non-state actors alike. A lack of political focus, patchy regulations, and inconsistent enforcement globally could pave the way for an act of nuclear terrorism. Additionally, as the demand for nuclear energy grows, so does the risk that individual countries could divert nuclear materials from peaceful purposes to develop clandestine nuclear weapons programs.
NTI’s Nuclear Materials Security Program works to strengthen global nuclear security and verifiably prevent the spread of nuclear materials that could be used to create a nuclear bomb. The program works closely with governments, industry, and other non-government organizations to better secure vulnerable nuclear materials or eliminate them where possible. It also seeks to identify and implement new approaches to the nuclear fuel cycle, reducing proliferation risks, and fostering responsible nuclear energy growth. NTI establishes practical solutions by convening leaders, developing actionable recommendations, and tracking progress on commitments, taking into account each stage of the nuclear fuel cycle and advanced reactor development.
Our work includes:
Generating new solutions for spent fuel waste management and addressing broader fuel cycle concerns
Building a safer, more secure, and more proliferation-resistant nuclear fuel cycle
Breaking down gender barriers and making gender equity a working reality
Strengthening the global nuclear security system
Minimizing the use of HEU in civil applications
Engaging a diverse group of states to develop innovative monitoring and verification solutions
Improving verification to prevent nuclear weapons proliferation
Building a framework for assurance, accountability, and action
During the 17th meeting of the Global Dialogue, participants developed plans to ensure successful outcomes at ICONS and leverage that momentum to reinvigorate nuclear security internationally.
NTI advanced key principles from a recent report that outlines pathways for the responsible, sustainable, and effective development of new nuclear projects and industries in embarking countries.
At this critical juncture for action on climate change and energy security, 20 NGOs from around the globe jointly call for the efficient and responsible expansion of nuclear energy and advance six key principles for doing so.
Experts from NTI and the China Arms Control and Disarmament Association (CACDA) gathered at the State Nuclear Technology Centre (SNSTC) outside of Beijing for the first in-person meeting of the China-U.S. Track II Dialogue on Nuclear Security since the COVID-19 pandemic.
To make good on their COP28 pledge, countries need a new approach to building, regulating, and financing nuclear technology.











