Iran

Country Spotlight
Iran’s nuclear ambitions have been a focus of international diplomacy for decades. Faced with accusations of nuclear weapons pursuits in violation of its NPT commitments, Iran concluded a 2015 agreement, the JCPOA, to restrict its nuclear program. However, the 2018 U.S. withdrawal from the deal and subsequent Iranian violations cast doubt on the deal’s future.
See Iran's performance in
Region Middle East and North Africa
128.3 kg Uranium enriched to 60% as of October 2023
4,486.8 kg Total stockpile of enriched uranium as of October 2023
2,000 km Self-imposed range limit on ballistic missiles
Nuclear
- NEWS: In February 2024, Iran announced the start of construction of four new nuclear power plants with a total capacity of 5,000 megawatts; Iran plans to produce 20,000 megawatts of nuclear energy by 2041
- Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) concluded in 2015 to restrict Iran's nuclear program in exchange for sanctions relief
- Possesses complete uranium fuel cycle capabilities
- Nuclear program and personnel have been targets of sabotage and assassinations


Overview of the Nuclear Disarmament Resource Collection
Biological
- Denies acquisition or production of biological weapons
- Has sophisticated biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries
- Engages in dual-use activities which "raise concern" with U.S. government

Tutorial on Biological Weapons Nonproliferation
Iran Biological Overview
Missile
- Large, increasingly sophisticated ballistic missile and space launch programs
- Initially received foreign assistance, particularly from North Korea, but today possesses indigenous capabilities
- Supplies missiles and rockets to partner and proxy groups in Iraq, Lebanon, Syria, and Yemen

The CNS Iran Missile and SLV Launch Database
No, Iran Is Not Pursuing an ICBM (Yet)
Chemical
- Suffered severe losses from Iraqi chemical weapons use during the Iran-Iraq War
- Acknowledges development of limited chemical weapons capability in 1980s but denies ever weaponizing or using chemical weapons
- Rejects U.S. claims that Iran supplied Libya with chemical munitions in 1980s

Iran Chemical Overview

On Iran and North Korea: Don’t trust, and verify, verify, verify
Treaties and Regimes Memberships
- NTI
- CNS
 Iran
IranAerospace Industries Organization (AIO)
- Missile
Amirkabir University of Technology
- Nuclear
Anarak Waste Storage Facility
- Nuclear
Arak Nuclear Complex
- Nuclear
Ardakan Yellowcake Production Plant
- Nuclear
Atomic Energy Organization of Iran (AEOI)
- Nuclear
Bakhtaran Missile Base
- Missile
Bandar Abbas
- Missile
Bandar Abbas Uranium Production Plant (BUP)
- Nuclear
Bank Sepah
- Missile
Bonab Atomic Energy Research Center
- Nuclear
Bushehr Nuclear Power Plant (BNPP)
- Nuclear
Defense Industries Organization (DIO) (Missile)
- Missile
Defense Industries Organization (DIO) (Nuclear)
- Nuclear
Fajr Industrial Group
- Missile
Fordow Fuel Enrichment Plant
- Nuclear
Fuel Enrichment Plant (FEP)
- Nuclear
Fuel Fabrication Laboratory (FFL)
- Nuclear
Graphite Sub-Critical Reactor (ENTC GSCR)
- Nuclear
Heavy Water Production Plant (HWPP)
- Nuclear
Heavy Water Zero Power Reactor (ENTC-HWZPR)
- Nuclear
Imam Ali Missile Base
- Missile
Imam Hussein University (IHU)
- Nuclear
Imam Khomeini Space Center
- Missile
Institute for Studies in Theoretical Physics and Mathematics (IPM)
- Nuclear
Isfahan (Esfahan) Nuclear Fuel Research and Production Center (NFRPC)
- Nuclear
Isfahan (Esfahan) Nuclear Technology Center (INTC)
- Nuclear
Isfahan Missile Complex
- Missile
Lashkar Ab’ad
- Nuclear
Light Water Sub-Critical Reactor (ENTC-LWSCR)
- Nuclear
Miniature Neutron Source Reactor (MNSR)
- Nuclear
Ministry of Defense and Armed Forces Logistics (MODAFL)
- Missile
Natanz Enrichment Complex
- Nuclear
Parchin Military Complex (Missile)
- Missile
Parchin Military Complex (Nuclear)
- Nuclear
Pilot Fuel Enrichment Plant (PFEP)
- Nuclear
Qom Waste Disposal Site
- Nuclear
Saghand Uranium Mine
- Nuclear
Semnan Missile Complex
- Missile
Shahid Bakeri Industrial Group
- Missile
Shahid Hemmat Industrial Group
- Missile
Shahroud Missile Test Site
- Missile
Shiraz Missile Plant
- Missile
Tabriz Missile Base
- Missile
Tehran Nuclear Research Center (TNRC)
- Nuclear
Tehran Research Reactor (TRR)
- Nuclear
Uranium Conversion Facility (UCF)
- Nuclear
Yazd Radiation Processing Center (YRPC)
- Nuclear
Zirconium Production Plant (ZPP)
- Nuclear
Analysis
Iran

The CNS India and Pakistan Missile Launch Databases
Database of Indian and Pakistani missile tests including the date, time, missile name, launch agency, facility name, and test outcome. (CNS)
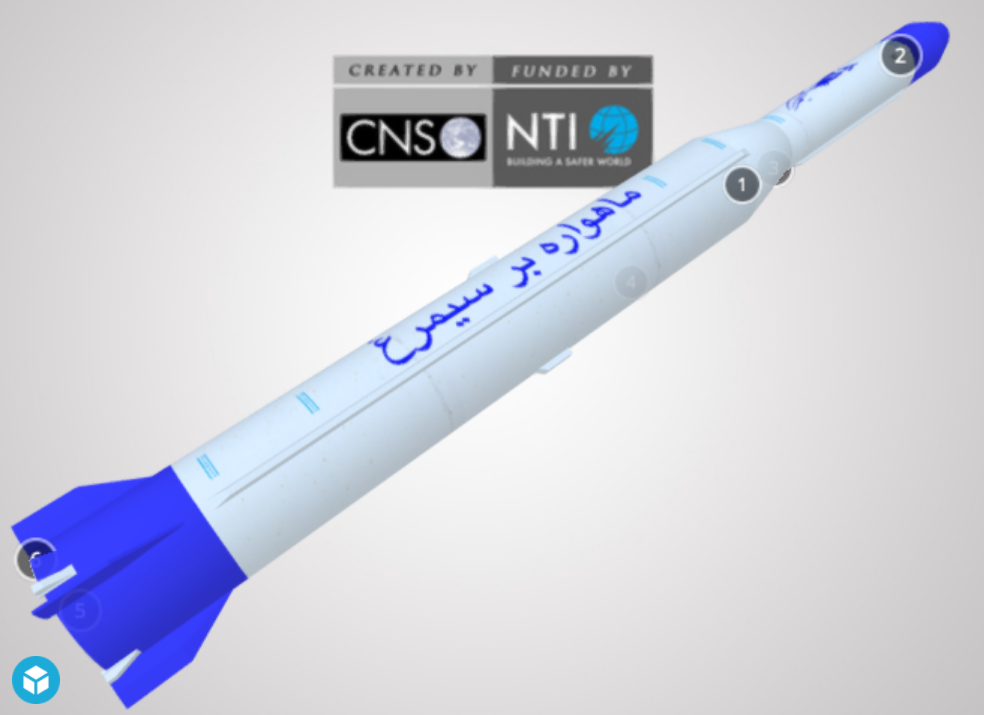

Iranian Ballistic Missile Models

Iranian Centrifuge Model Collection

Education Center
Extensive resources on nuclear policy, biological threats, radiological security, cyber threats and more.
Sources
Institute for Science and International Security (ISIS), “Iran’s Nuclear Program: 1950s and 60s: Atoms for Peace,” isis-online.org.
Institute for Science and International Security (ISIS), “Iran’s Nuclear Fuel Cycle,” isisnucleariran.org.
U.S. Department of State, “Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action,” https://2009-2017.state.gov.
U.S. Department of State, “Adherence to and Compliance with Arms Control, Nonproliferation, and Disarmament Agreements and Commitments,” April 2023, www.state.gov.
International Atomic Energy Agency, Board of Governors, “NPT Safeguards Agreement with the Islamic Republic of Iran,” GOV/2023/58, November 15, 2023, www.iaea.org.
Stephanie Liechtenstein, “UN agency report says Iran has further increased it uranium stockpile,” Associated Press, November 15, 2023, www.apnews.com.
“Iran begins building 4 more nuclear power plants,” Associated Press, February 1, 2024, https://apnews.com.
